Object Storage
Object Storage is Sealos' built-in object storage service, which is primarily used to store and manage unstructured data.
Currently, Object Storage has the following features:
- Upload files to bucket
- Download files from bucket
- Expose the access permission of the bucket
- Use SDK to access bucket
- Monitors bucket resource metrics
Quick start
Upload files to bucket
Go to Object Storage
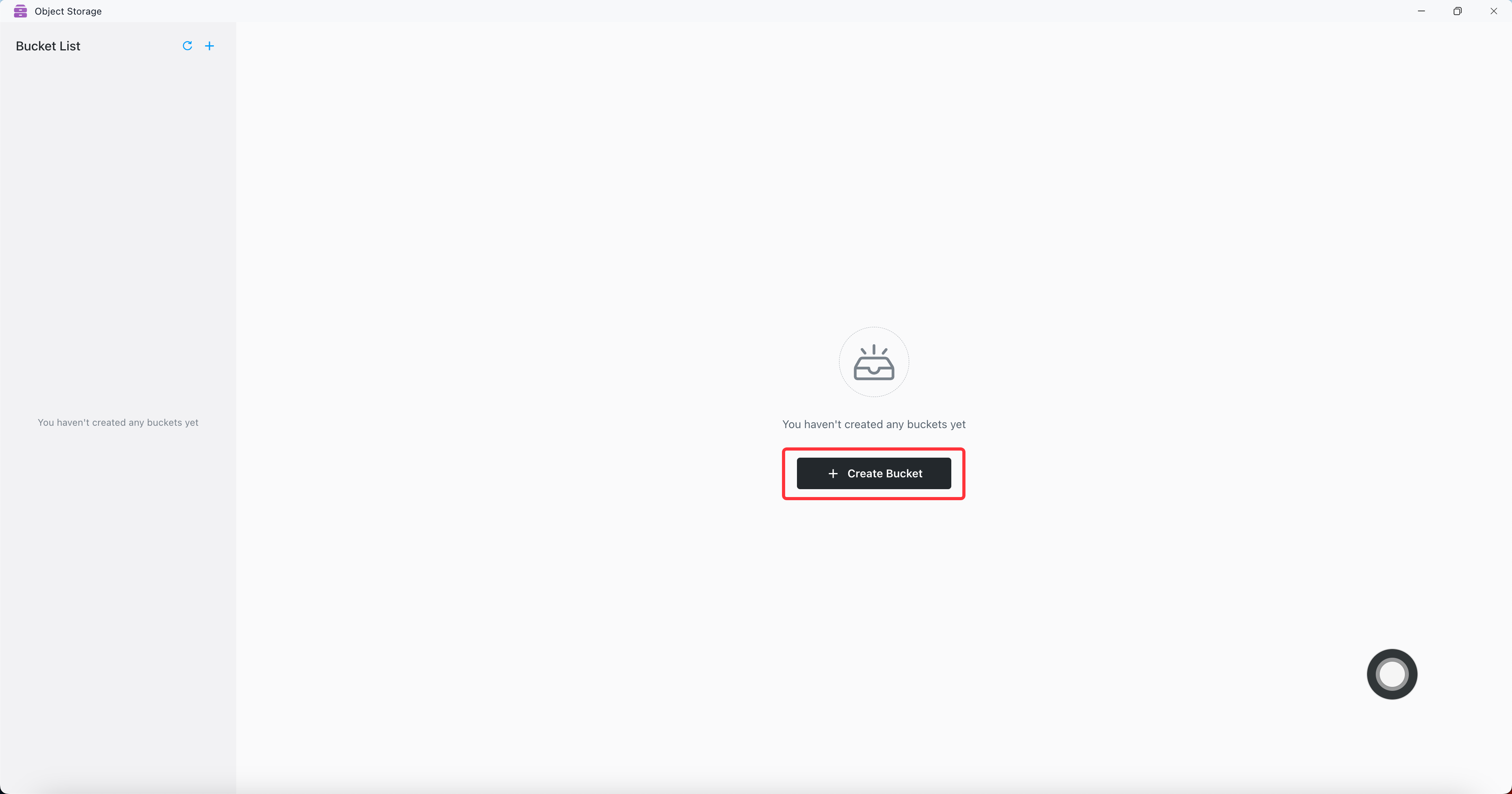
Create a bucket
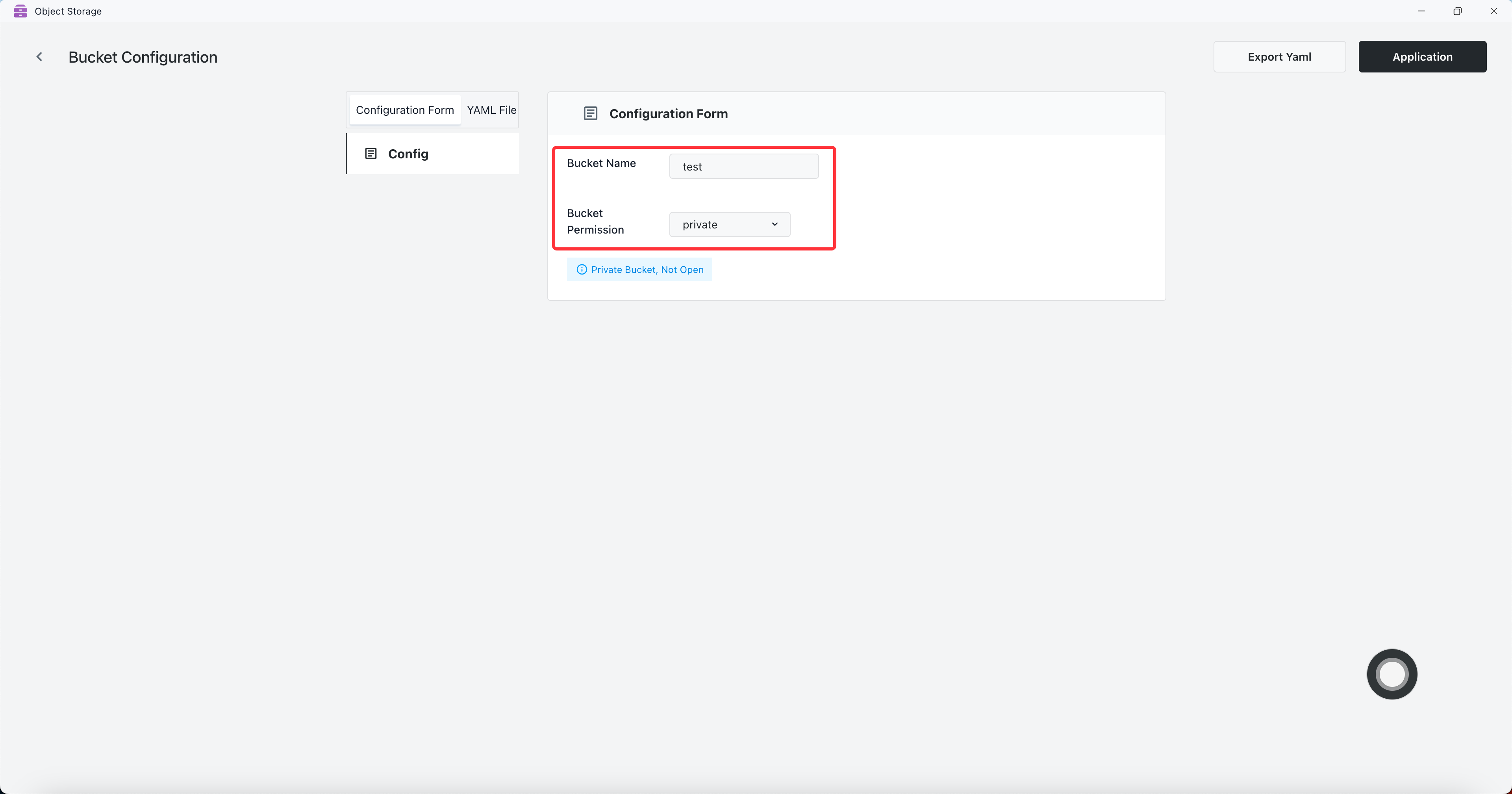
Set bucket name to test and permission to private
Bucket is created successfully
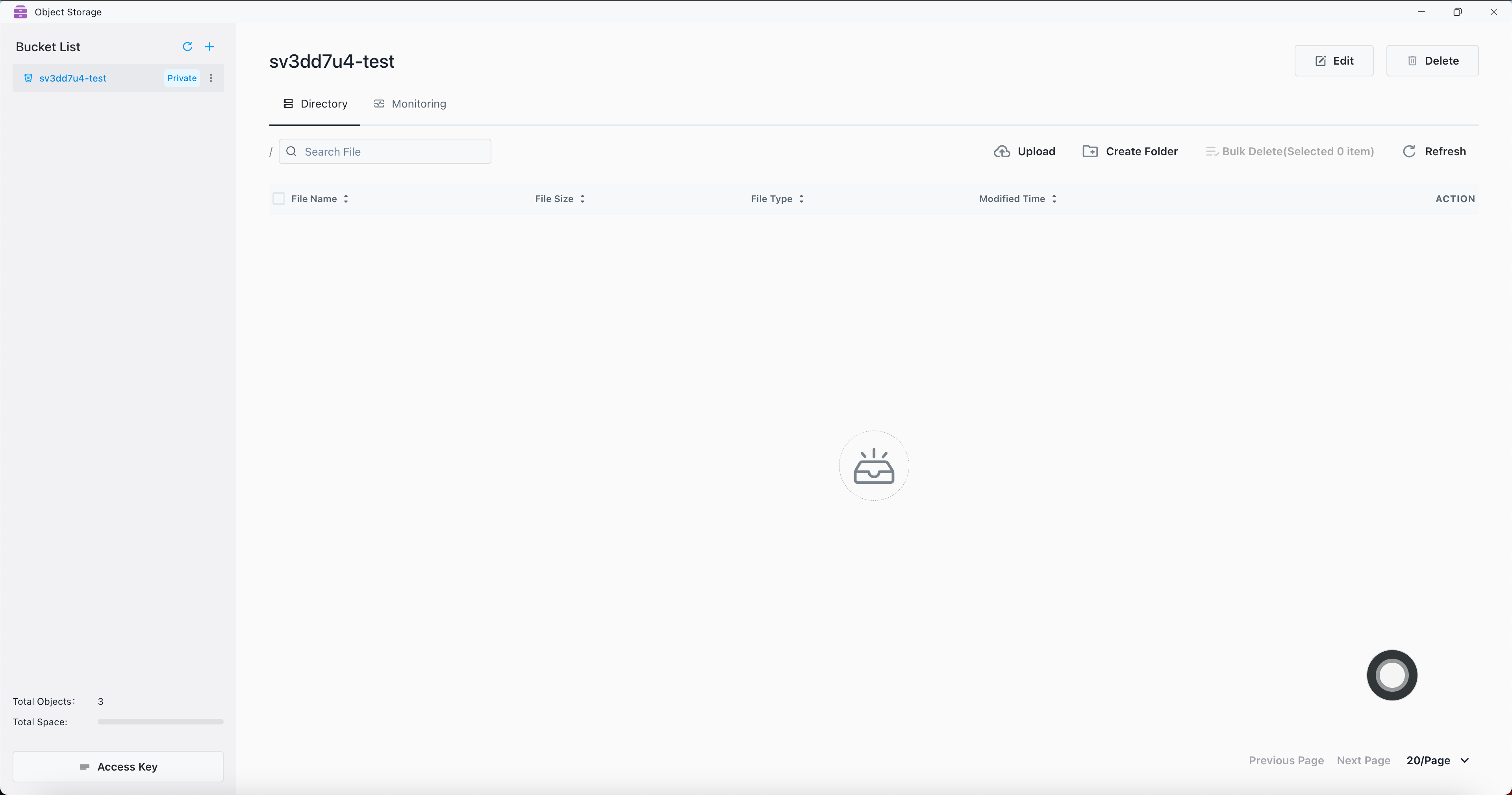
Upload file
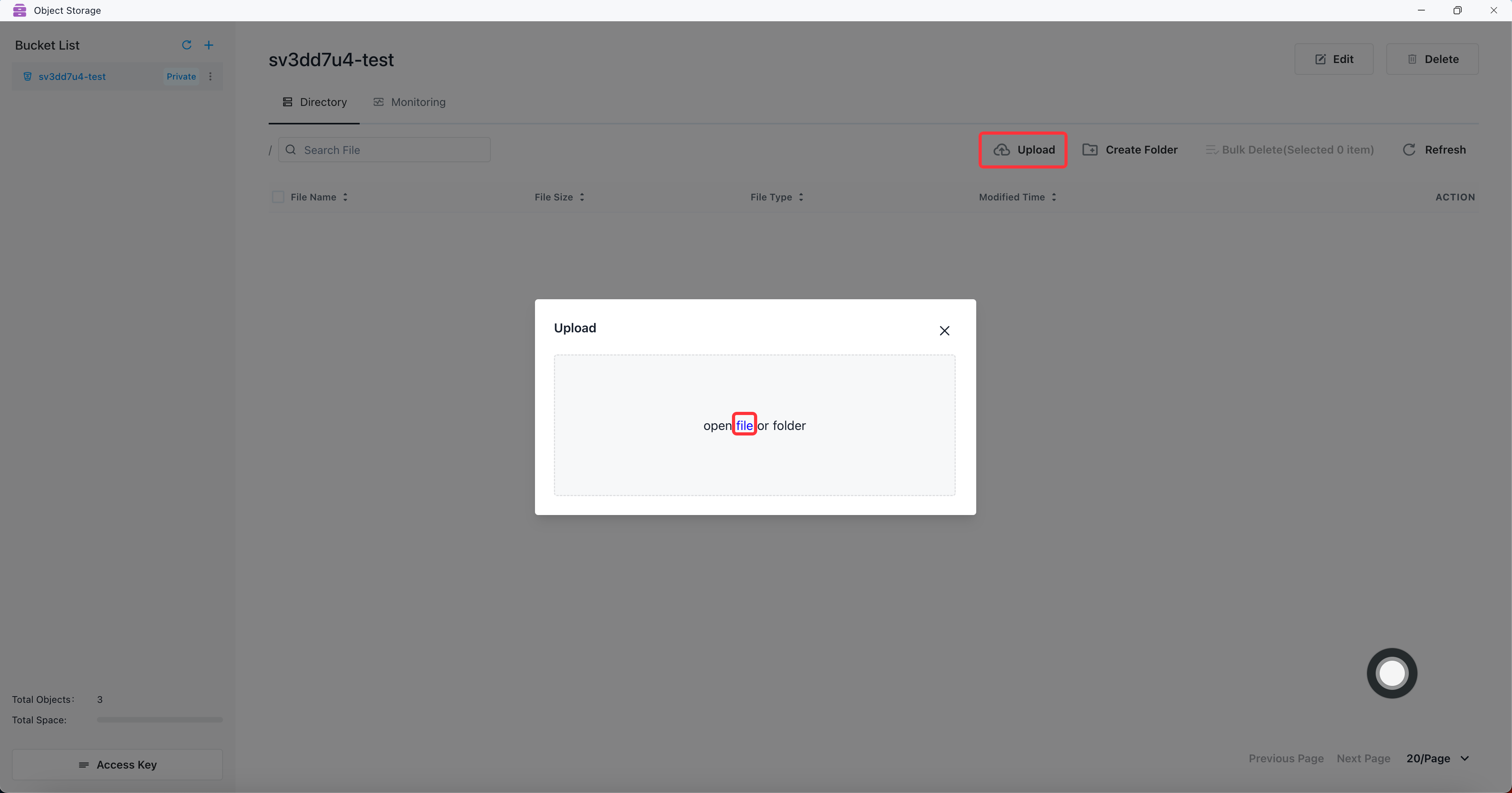
File uploaded successfully
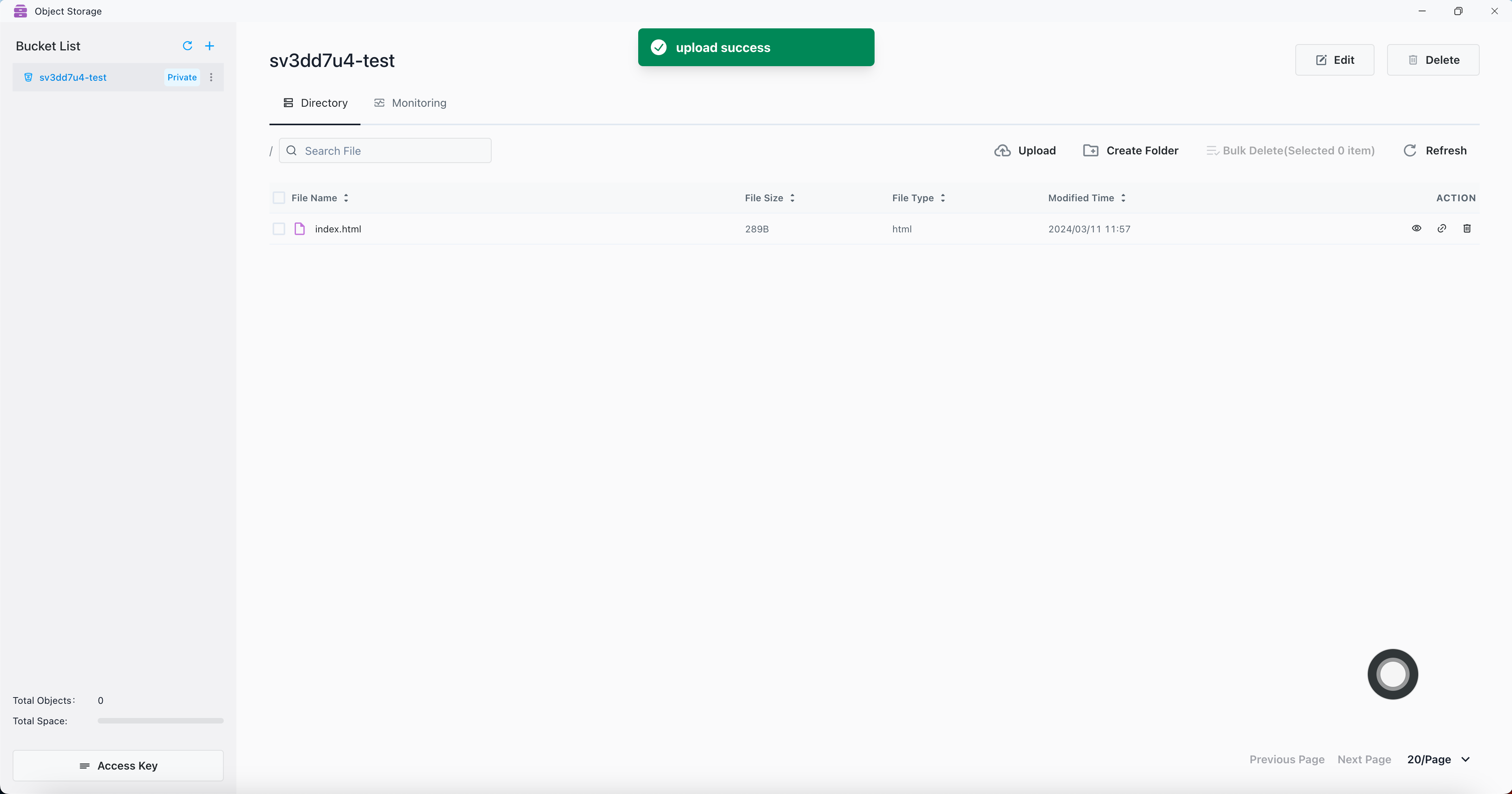
Expose the access permission of the bucket
Click the Edit button
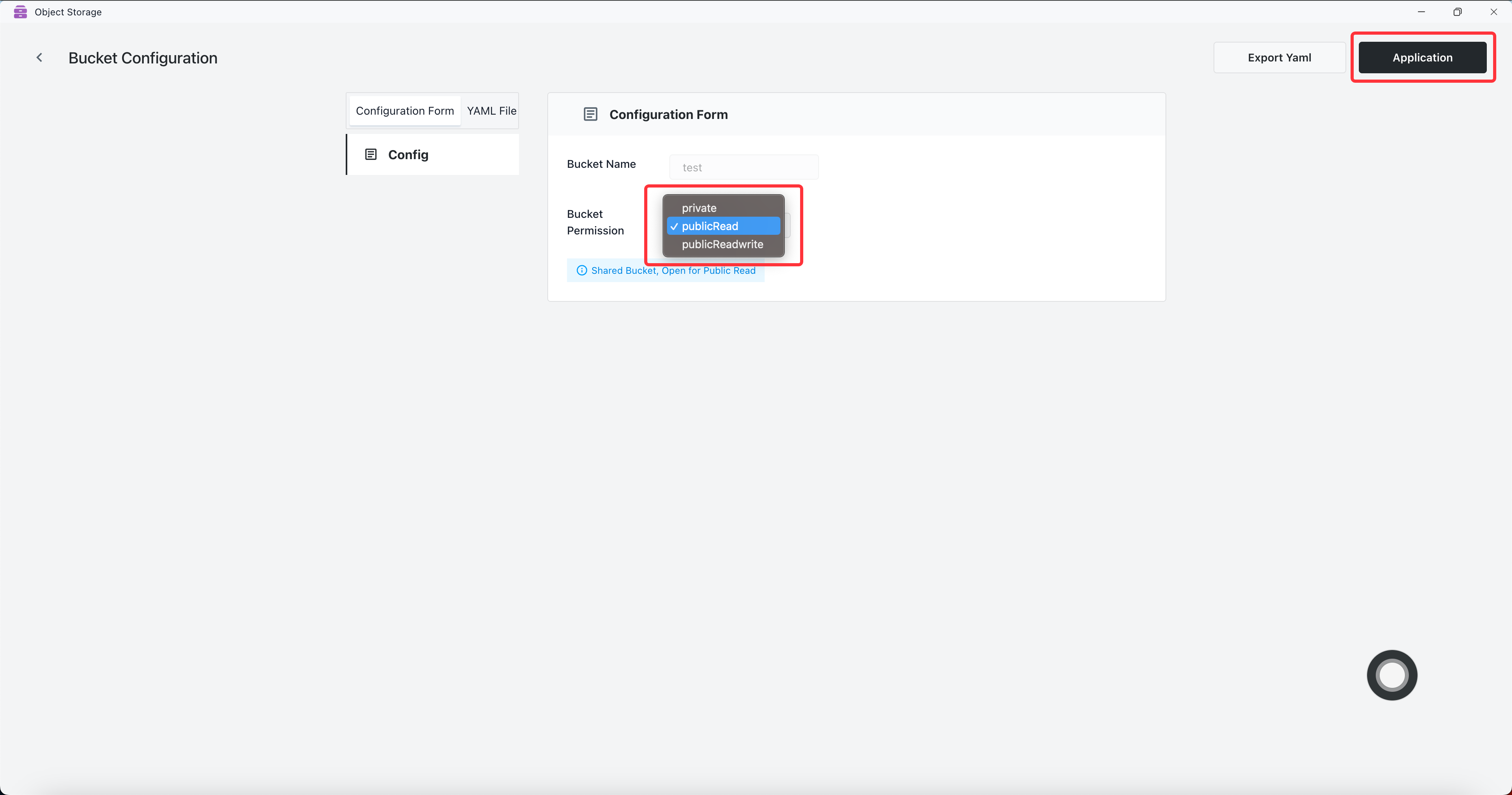
Set Bucket Permission to publicRead and click the Application button
Copy file link

Paste to browser address bar to access files
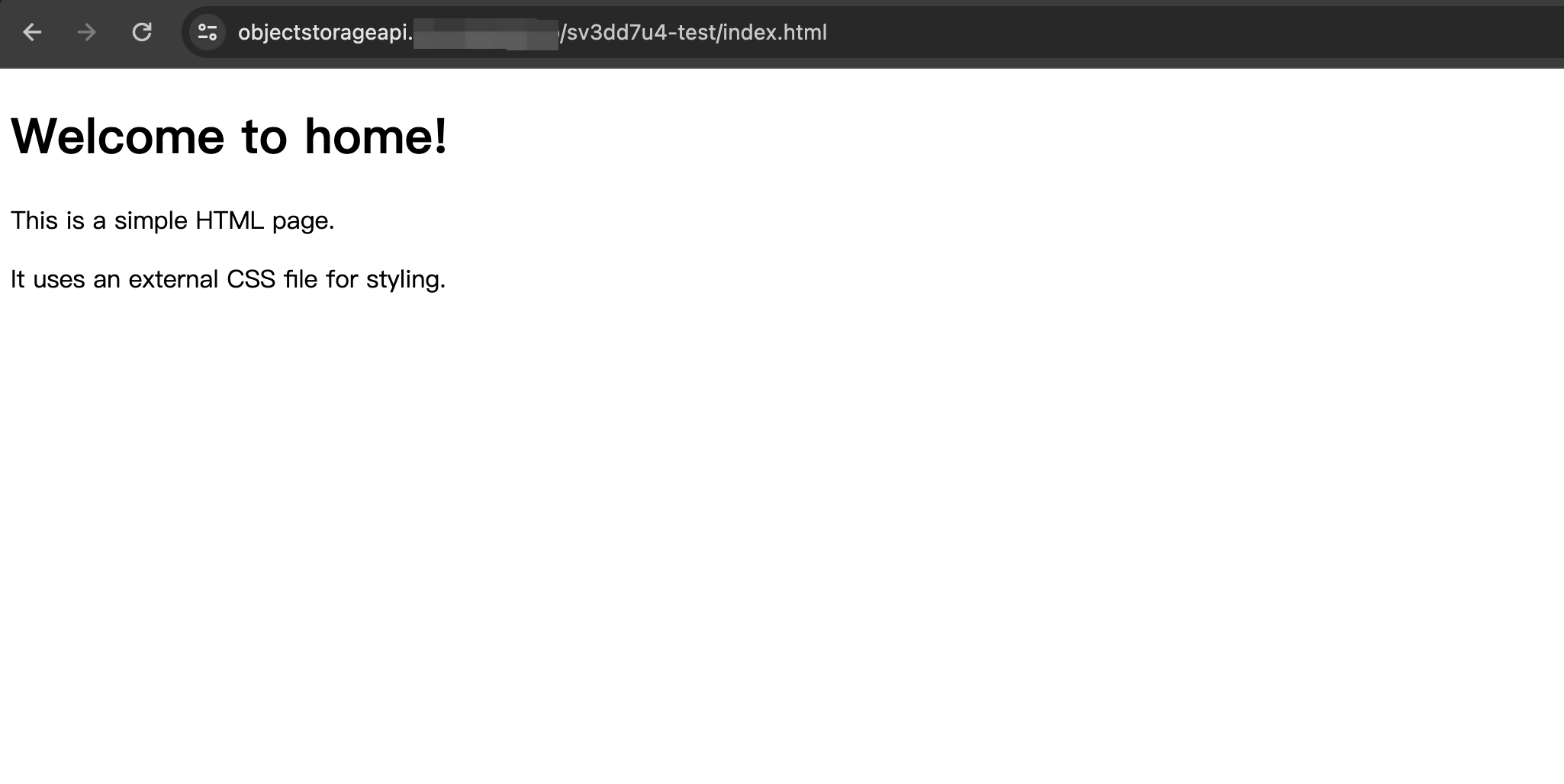
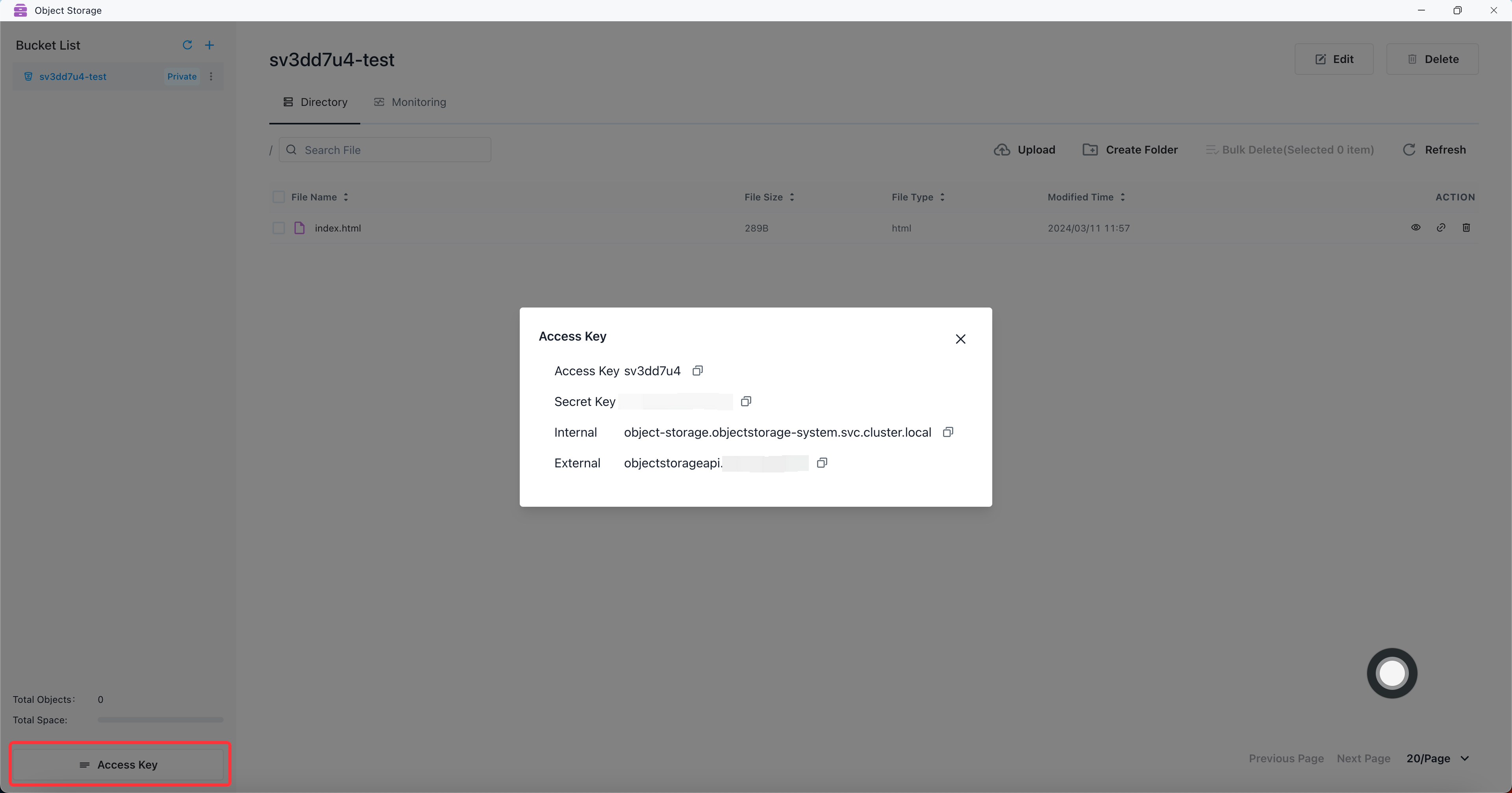
View the access key configuration
An Object Storage user consists of a unique access key (username) and corresponding secret key (password). Internal is
the internal access address of Object Storage, and External is the external access address of Object Storage.
Use SDK to access bucket
The SDK requires three parameters to access bucket: AccessKey, SecretKey, and Endpoint (Internal or External). If the Region parameter is required, us-east-1 is used by default.
Go Client SDK
Detailed documentation reference: https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/API.html
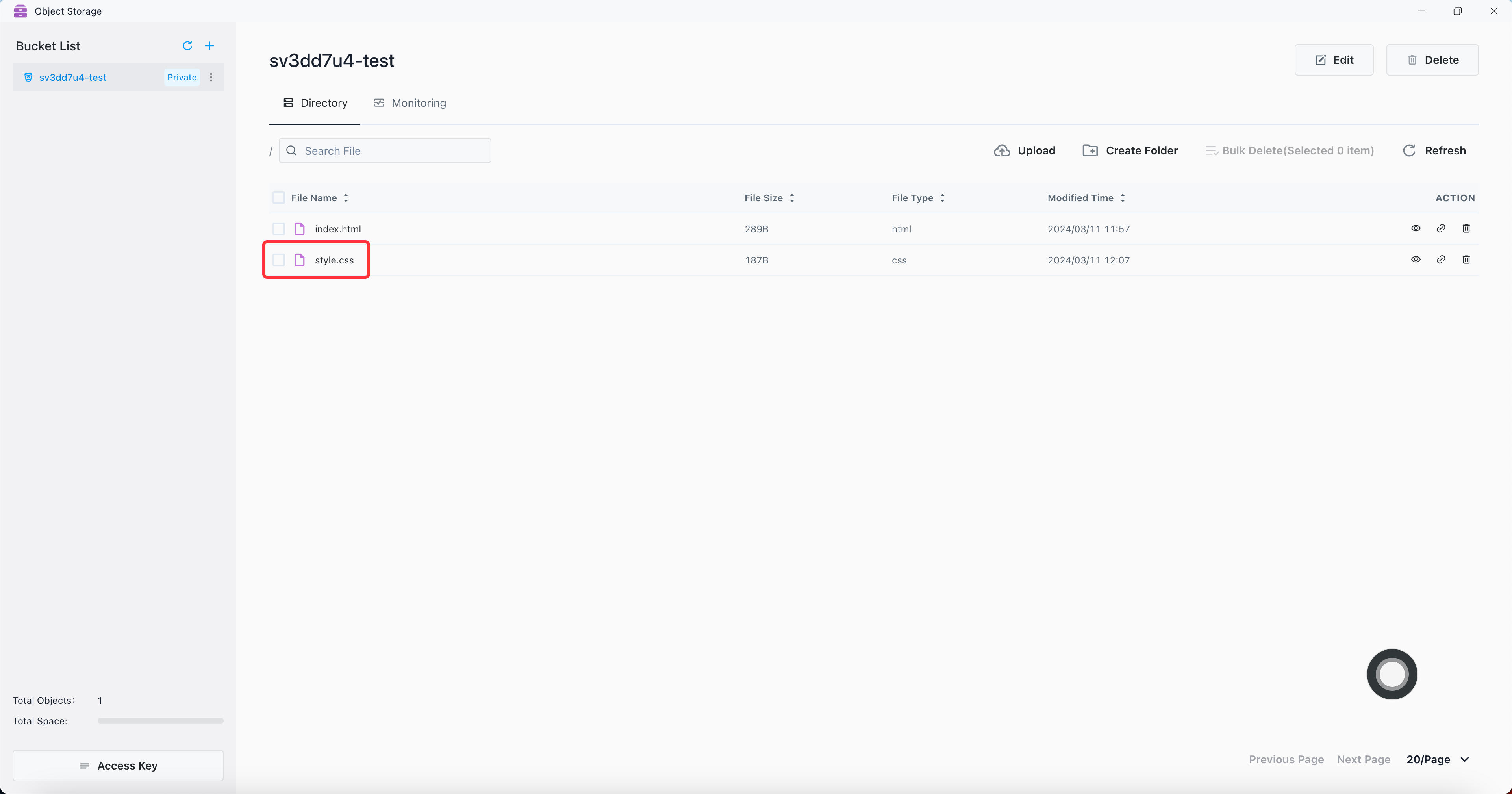
Example: Use the Go Client SDK to upload the style.css file to the sv3dd7u4-test bucket, and set the endpoint to the external address. If the service is deployed in the K8s cluster, you can change the endpoint to the internal address.
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
)
import "github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
import "github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials"
func main() {
endpoint := "objectstorageapi.xxx.xxx.xxx"
accessKey := "xxxxxxxx"
secretKey := "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
// init minio client
minioClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKey, secretKey, ""),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// get local file
file, err := os.Open("./style.css")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
fileStat, err := file.Stat()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// put object
uploadInfo, err := minioClient.PutObject(context.Background(), "sv3dd7u4-test", "style.css", file, fileStat.Size(), minio.PutObjectOptions{ContentType: "text/css"})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println("Successfully uploaded bytes: ", uploadInfo)
}
File uploaded successfully
Java Client SDK
Detailed documentation reference: https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/java/API.html
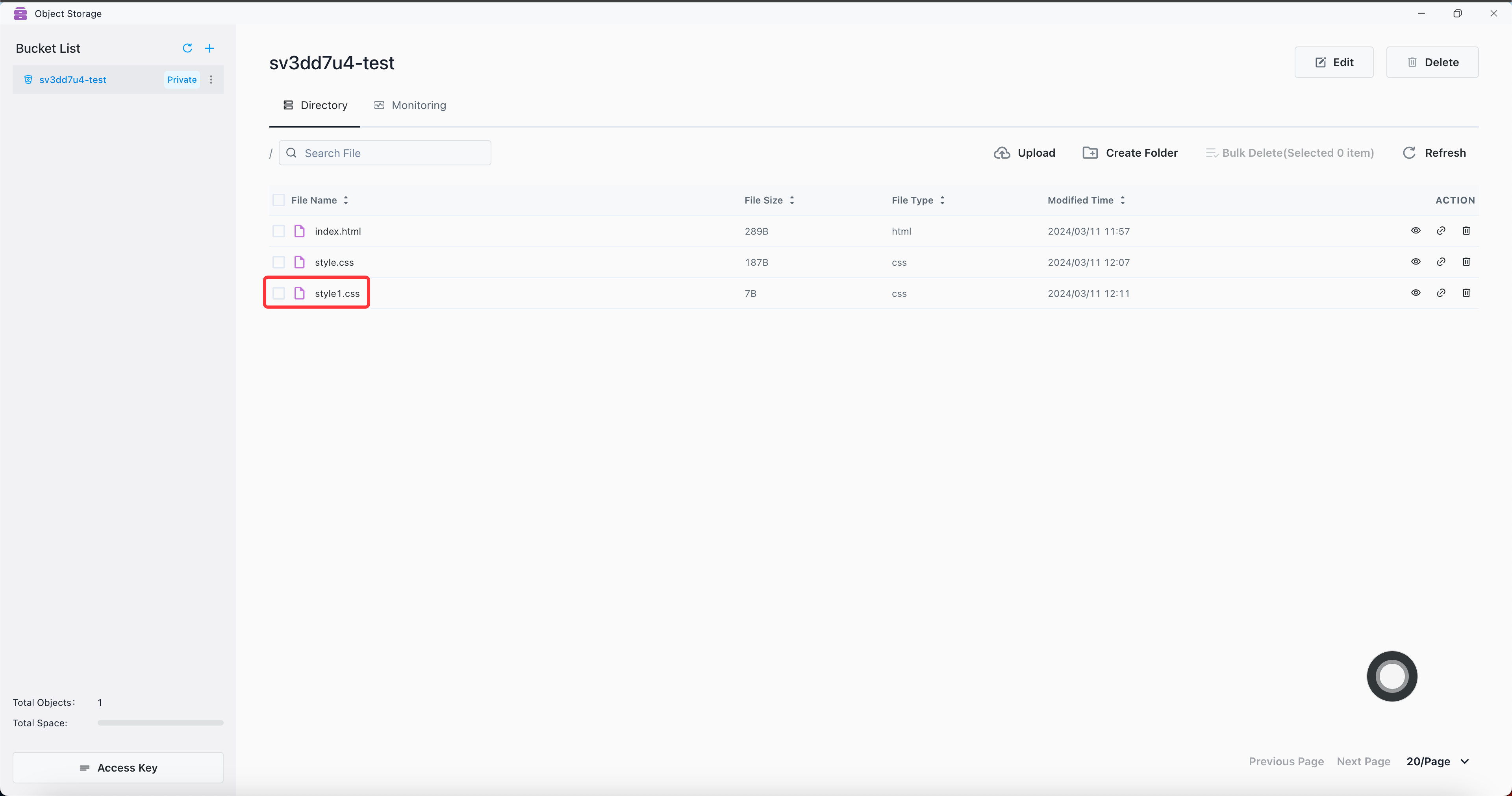
Example: Use the Java Client SDK to upload the style1.css file to the sv3dd7u4-test bucket, and set the endpoint to the external address. If the service is deployed in the K8s cluster, you can change the endpoint to the internal address.
<dependency>
<groupId>io.minio</groupId>
<artifactId>minio</artifactId>
<version>8.5.9</version>
</dependency>
package org.example;
import io.minio.MinioClient;
import io.minio.UploadObjectArgs;
public class FileUploader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MinioClient minioClient =
MinioClient.builder()
.endpoint("https://objectstorageapi.xxx.xxx.xxx")
.credentials("xxxxxxxx", "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx")
.build();
minioClient.uploadObject(
UploadObjectArgs.builder()
.bucket("sv3dd7u4-test")
.object("style1.css")
.filename("src/main/java/org/example/style1.css")
.build());
System.out.println("Successfully uploaded bytes.");
}
}
File uploaded successfully
Omit other language SDK
Detailed documentation reference: https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/minio-drivers.html